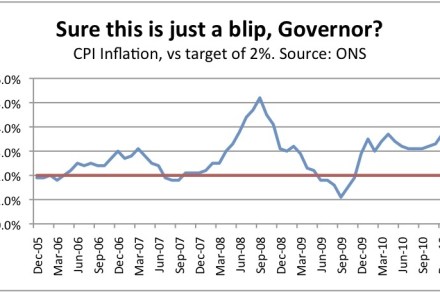
Inflation: how the nightmare will continue
Each month, inflation numbers come out and seem to surprise everyone – except the chosen few who have access to the forecasts. So I thought we’d share with CoffeeHousers what is all too seldom put on public record: forecasts for inflation and base interest rates. It might be useful to anyone thinking of taking out a fixed rate mortgage deal. These forecasts are from Michael Saunders at CitiGroup, whom I regard as one of the best in the business. Pretty much every analyst thinks that interest rates will soon start a relentless march back to 5 per cent, so these 3 per cent fixed rate deals we’re getting right now